Secure Network Cloud Ecosystem – 2023 Dynamics
Navigating Your Journey When There Is No Destination
People frequently talk about goals and objectives but for this author, it’s the journey experienced day-to-day that is of more interest. Especially as most thoughts about the future are based on a predictable past. This has never been more appropriate than when dealing with the network ecosystem.
This article is a review of today’s complex, seemingly chaotic network landscape. If nothing else, it’s important to be at ease with living with business and technologies in a state of constant migration—because that’s exactly where we are. The intention is to provide some guidance on your journey. To begin, it’s important to start by looking at today’s reality about our Network Cloud Ecosystem.
In my recent ISE Magazine article on holistic cybersecurity,1 we looked at Zero Trust being the only viable solution for the perimeter-less network. We called out the many potential enforcement points as we laid out the principal elements of the ecosystem as the backdrop in Figure 1. It also called out the dynamics behind its evolution (migration to the network cloud).
Despite the complex and evolving nature of our network environment, there are several other factors in play that are important to understand. These may not be obvious and are either overhyped or not spoken of at all. These are:
- Secure Access Service Edge and Secure Service Edge
- Standards and Open-Source Challenges
- Newly Available Standards
- A Layered Business Architecture
- Service and Cloud Provider, Integrator and End-user perspectives
Secure Access Service Edge and Secure Service Edge
Since December 2019, when Gartner’s SASE blog2 envisaged a set of technologies, the network community was given a direction—the possibility of the secure integrated network ecosystem. A great idea that has created masses of hype and multibillion dollar analyst predictions. Soon after COVID-19 hit and Zero Trust became a necessity, SASE became even more important. Both were equally misinterpreted (I think I’m being polite). As we said at the beginning, it’s a journey that needs a 2023 reality check to get past the hype.
For those living under a rock for the last three years with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), Gartner called out (but did not define) SD-WAN “Overlay” services and network services “such as” Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Firewall as a Service (FWaaS) and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and has termed it all as SASE. Essentially, SASE is a package of technologies including the core abilities above with the ability to identify sensitive data or malware and the ability to decrypt content at line speed, with continuous monitoring of sessions for risk and trust levels.
Today and tomorrow, that possibility is becoming a reality with around 20 suppliers, integrators, and service providers taking the journey to SASE. However, any claims of compliance to the SASE model should be viewed with caution because frankly it’s a combination of services, not a definition of a standardized, cohesive, implementable framework. As you read the product reviews of solutions marketed as SASE, you should view them as earnest attempts at implementations that will, or may, eventually encompass all the elements but for now represent some of the required components. Implementations themselves often blur the distinctions between the categories, none of which actually have an agreed standard definition, being proprietary in nature! Even the recent NIST “Guide to a Secure Network Landscape4” should be read with this in mind.
But wait, there’s more. Not only are there no standardized definitions but newer ideas have legitimately been rolled into one offering, for example, CASB and RBI (Remote Browser Isolation). RBI is a cool function, separating users’ devices from the act of Internet browsing by hosting and running all browsing sessions on a remote cloud-based, and hopefully secure, container. It helps prevent malware from being inadvertently loaded onto end user systems. It also means that data can be screened to avoid exfiltration of sensitive data or access to middle box functions and as a phishing defense. It’s also an efficient way and place to implement a Zero Trust End Point.
Perhaps daunted by the monster they had created, Gartner later created a milestone in the SASE roadmap termed Secure Service Edge (SSE) consisting of just SWG, CASB and ZTNA. Capabilities included access control, threat protection, data security, monitoring, and use control enforced by network and API-based integration. SSE is primarily delivered as a cloud-based service and may include on-prem or agent-based components. In March 2022, Gartner created a new magic quadrant summarizing 11 players in this space.
Industry reviews of product progress. This article provides a context for your reading. I cannot vouch for the analysis:
- Software Testing’s top 11 SASE Vendors3
- TechRadar’s Top SASE vendors5
- Netify’s top 10 SASE vendors6
- Expert Insight’s top 10 SASE vendors7
- Gartner’s Magic quadrant features 11 SSE companies (Feb 22)8
It's such a temptation for suppliers or service providers to wrap their products into “unique all-encompassing solutions” with the actual value, the products can be lost. I.e., the guidance of this article is to ignore any “complete SASE/SSE solution” hype and focus on matching what a product actually does against your current and anticipated business requirements. We will discuss later a layered business architecture model that will handle migration and technology changes to help with such decisions.
As I said upfront, this is a journey and it’s one worth taking. SASE and SSE are finding their way in the world.
Standards and Open-Source Challenges
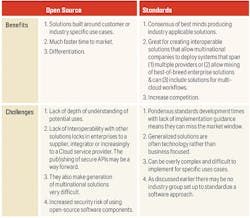
Having been on both sides of this discussion, it’s clear that both industry standards and open source have benefits and challenges. (See Figure 2.)
It’s also clear that if time to market is key then open source is the fastest but not often the cheapest approach. If multinational or multi-cloud approaches are critical, then standards-based approaches are advisable. Solutions that appear later based on standards can then be built in as a migration path.
In the next section, we look at some very recent standards that can be used to bring services and products that enable both SASE deployment and Zero Trust Enforcement to many points in the ecosystem including operational networks.
New Standards for the Secure Network Cloud Ecosystem
There are several standards related to implementing secure network ecosystem services. The SD-WAN service is well-established and two are new.
The MEF (MEF.net) has produced standards for more than two decades and some recent ones are available to network equipment suppliers, security providers and service providers.
The latest iterations include MEF 70.19 SD-WAN Service Attributes and Service Framework. This developing standard defines the externally visible behavior of an SD-WAN Service based as an agreement between an SD-WAN subscriber (buyer) and a service provider (seller) agreement on the values of a set of SD-WAN service attributes. This was published in 2021.
In November 2022, the MEF also published its standard MEF 11810: A Zero Trust Framework and Service Attributes. Its initial intention covers many use cases of potential Zero Trust-based services. These attributes enable services to implement Zero Trust principles and strategies into a network service deployed anywhere in the network. This is game changing. For instance, it could also be applied in Zero Trust-based services such as ZTNA, as part of the aforementioned SASE and also in areas of enterprise operational networks. This standard handles user identity, authentication, access control based on user roles and attributes, policy enforcement at policy endpoints and continuous monitoring as shown in Figure 3. It handles interactions between subject and target actors that can be users, applications, or devices such as IoT devices in operational networks. It enables standardization between applications and multi-cloud and computer edge workflows. The author of this article was privileged to be a contributor to this important standard over the last two years.
In November 2022, The MEF also published its SASE service and service attributes definition (MEF 117)11 by defining a standard combining security functions and network connectivity as an enabler of SASE services. It defines a service framework and specifies service attributes that need to be agreed between a service provider and a subscriber for SASE services, including security functions, policies, and connectivity services.
These specifications, in conjunction with proprietary SWG, CASB, FWaaS and RBI services, can be the basis of a robust SASE offering and a far-reaching enterprise network solution.
A Layered Business Architecture
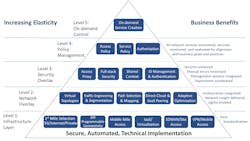
From an end-user’s organizational perspective, particularly larger enterprise and government bodies, the focus is on business agility, cost and, of course, security. This is an important topic for the Open Networking Group (ONUG.net). ONUG represents the voice of the enterprise providing that community with guidance on the evolving network cloud. The Network Cloud Working group, of which this author is a member, recently published a layered business Network Cloud Playbook.12 (See Figure 4.) This is driven by business policy and is intended to be capable of being able to replace network elements and infrastructure as dictated by changes in policies and on demand. It ties back to this article’s theme that network journey is never complete but in a constant state of migration. Its intention is to empower enterprises and businesses in general to choose an infrastructure that supports their unique business requirements.
Service & Cloud Providers, Integrators, Suppliers and End-User Perspectives
The final piece of this article covers the market dynamics. This is important because it gives you the context of the sales and purchasing discussions. Everyone wants to be in control. If you are an Enterprise, then you will relate to the business-oriented Network Cloud Playbook. You may also like to visit my website (cybyr.com) covering the importance of taking a holistic approach to cybersecurity across your entire organization. I.e., SASE and Zero Trust are important but they only address a small part of the cybersecurity landscape. Cybyr.com also breaks news of the latest threats and explains 100+ cybersecurity terms.
From the perspective of service providers, cloud providers, integrators, equipment suppliers, software and security companies—everyone wants to be in control and will claim to have a complete solution and build a wall around you and your purchases.
There are many forces in play in the evolving, dynamic Secure Network Cloud Ecosystem, some business, some technical and many commercial as summarized in Figure 5.
For end-user organizations it comes down to budget, control, security, and your ability to contractually bind your suppliers to their performance and ability to deliver high performance, high security solutions no matter what they are called or branded. As they say in Zero Trust, Don’t Trust, Verify.
My hope is that my personal perspective gives a balanced view bringing some order to the incredibly fast-moving pace of network change. For the most part it’s important to enjoy the journey and be flexible as the path to the perfect network will likely keep taking new turns!
REFERENCES AND NOTES
1. https://www.isemag.com/network-reliability-testing-and-assurance-cybersecurity-safety/article/14287070/the-search-for-cybersanity
2. https://blogs.gartner.com/andrew-lerner/2019/12/23/say-hello-sase-secure-access-service-edge/
3. https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/top-sase-vendors/
4. https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-215.pdf
5. https://www.techradar.com/features/here-are-the-10-biggest-sase-vendors
6. https://www.netify.com/learning/who-are-the-best-rated-sase-vendors
7. https://expertinsights.com/insights/top-sase-solutions/
8. https://www.gartner.com/doc/reprints?id=1-2966J3JL&ct=220218&st=sb
9. https://www.mef.net/wp-content/uploads/MEF_70.1.pdf
10. https://www.mef.net/wp-content/uploads/MEF-118.pdf
11. https://www.mef.net/wp-content/uploads/MEF-117.pdf
12. https://onug.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/ONUG-Network-Cloud-White-Paper.pdf
About the Author
Mark Fishburn
Provider of Strategic Network, Cybersecurity, Software, and Marketing Services
Mark is President of cybyr.com and has five decades of experience in software, networking, and security. He is a member of ONUG, Mplify, and CSA network and security working Groups, CISA contributor and publisher of the Holistic Cybersecurity book: Hey Who Left The Back Door Open? For more information, or to give feedback, email [email protected] or follow him on LinkedIn.