SPONSORED CONTENT
Since 1996, private sector telecoms have invested $1.5 trillion in capex to deliver or improve broadband services, according to USTELECOM. That’s $75 billion every year. Is that investment going to the right place? How can companies determine that their investment will maximize revenue growth or improve the customer experience?
The data to make these operational decisions exists today. A geographical information system (GIS) can help collect, visualize, and analyze relevant data to better understand relationships, patterns and trends. Understanding market dynamics and making intelligent capital investments with the myriad of new network technologies is a complex process. The more complex the problem, the more value GIS delivers.
Data Visualization
GIS provides powerful data visualization to identify patterns and trends. A typical example is a wireless coverage map which when combined with an overlay of dropped or blocked calls can provide a heat map, giving insight into locations that lack adequate signal coverage. Once these underserved areas are identified, capital funding for network expansion can be implemented to augment the existing network coverage. (See Figure 1.)
Figure 1.
Analytics
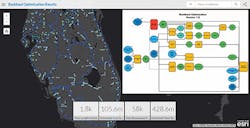
Applying the inherent modeling and analytical capabilities of GIS, telecoms can predict how the planned capital investment will improve service. The same capabilities can be applied to predict severe weather impact on network performance or potential outages. Spatial analytics can also reduce time and cost by automating many manual processes. Using spatial models, GIS can easily handle complex analytics that require evaluation of a large number of network sites while performing many repetitive calculations. These models automate complex analytics by stringing together sequences of geoprocessing tools. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 2.
Decision Making
Areas where automated models are proving especially useful is evaluating network services options at multiple sites. Examples include evaluating cell site fiber backhaul options or identifying ideal locations for WiFi hotspots for cellular offload. Requests covering dozens or hundreds of sites can be run in minutes replacing manual processes that previously required hundreds of person-hours of engineering resources. This can be a significant time and money saver.
The Future of GIS
As the GIS technology continues to evolve, new and innovative datasets will be brought to market. In turn, the availability of new spatial data will drive more advances in GIS technology. One of the areas of development that is already under way is 3D GIS. This added dimension will provide a virtual reality window, helping us visualize and analyze in ways we never thought possible. Another area that will be improved is combining spatial analytics with real-time data. Companies are already exploring the application of GIS modeling techniques to provide recommendations on where to deploy SDN and NFV investments to optimize return on investment.
Telecoms are already using GIS to optimize network investment and operations. Learn more at esri.com/ISEMag.
About the Company: ArcGIS Software/Esri is the world leader in delivering a geographic information system (GIS) technology that enables enterprises of all sizes to think, analyze, and act geographically. The ArcGIS solution eliminates silos by connecting all the departments in an organization using an industry-standard, location mapping and geospatial analysis platform. Esri’s solutions for the Telecommunications industry provide on-screen, real-time visual information to effectively assess, plan, engineer and track network projects. Companies can access and share data through a single GIS platform enabling enhanced market forecasts and analysis, network planning, service coverage maps, field crew routing and network analysis. Whether you require a custom solution for your enterprise or need enhanced engineering tools, Esri has a platform to meet every need. For additional information on Esri’s solutions for Telecommunications visit www.esri.com/ISEMag.
Save
Save
Save
About the Author