The Role of Smart Antennas in Optimizing 5G
5G cellular networks promise to improve many aspects of wireless communications, supporting enhanced mobile services, greater scalability for IoT systems, and ultra-reliable communications for mission-critical applications. A portion of these benefits will be based on the evolution of 4G LTE technologies as well as unique capabilities enabled by 5G New Radio, or 5GNR, based on new infrastructure supporting mmWave RAN equipment.
Why Is 5G New Radio (5GNR) Important?
5GNR has the potential to provide much higher data rates in a range of several gigabits per second. Equally important, 5G will provide ultra-low latency (less than 1 millisecond delay) required for certain portable or mobile apps and services such as industrial automation, robotics, haptic Internet, and virtual reality. This will enable portability/mobility for many previously tethered-only applications and services such as streaming 4K video, real-time remote control, haptic communications, and more.
Smart Antenna architecture
This will be based largely upon unique capabilities enabled by 5GNR that will support Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (URLLC) for both mission-critical services and latency-sensitive consumer services. Some applications have a very low tolerance for latency. If there is too much packet delay, video becomes jittery and unwatchable, and critical communications, such as robot operations, become completely useable and even dangerous.
Accordingly, certain URRLC application areas, such as industrial automation and robotics, will benefit greatly from 5G. New use cases and business models will emerge, such as cloud robotics in which a robot may be operated in an untethered manner (e.g., uncaged and unconnected by wires) as well as remotely and without the need for proprietary user interfaces.
Technologies currently under development for self-driving cars may also be used to enable autonomous robots powered by 5G. Why is it important to support URRLC apps? For one, Mind Commerce sees the global 5G-enabled autonomous robot market alone becoming a $14.6 billion opportunity by 2023.
5GNR enables ultra-fast communications at the radio access network (RAN). However, backhaul to a centralized cloud is a potential weak link in terms of latency. Therefore, wireless carriers plan to deploy Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) to enable processing at the edge of networks. MEC will be indispensable in support of 5G, especially for 5GNR-enabled applications. Applications deemed mission critical require low latency that would otherwise be diminished without MEC. This is due to reduced need for app-driven backhaul.
5G Needs Smart Antennas
MEC is not enough to ensure optimization as 5G systems will also need Smart Antennas to optimize coverage, mobility, and minimize the need for hand-over from 5G to 4G RAN. Smart Antennas are useful to optimize LTE, but they are absolutely necessary to provide mobility support for many new and enhanced 5G apps and services such as virtual reality, self-driving cars, connected vehicles, and Voice over 5G (Vo5G).
5GNR, in particular, needs Smart Antennas, because it utilizes millimeter wave RF propagation. 5GNR involves a much lower wavelength (millimeter as compared to centimeter to a meter for LTE) and therefore a higher frequency. Physics dictates that higher frequencies need more power and/or more coverage as an RF signal fades more than a lower frequency signal. This is why there will need to be at least an order of magnitude more antennas than required for LTE. Putting this into perspective, the US will go from roughly 30,000 antennas to 300,000 or more nationally.
5G antennas will be found virtually everywhere in metropolitan areas, but it will not be enough. While dramatically increased coverage will surely support many early 5G applications, such as fixed wireless (ISP alternative, backhaul, and fronthaul), it will not be enough to support continuous 5G mobility coverage. This will be vitally important for certain applications such as self-driving cars and connected vehicle services.
Smart Antennas for 5G will improve coverage and optimize capacity by focusing RF signals where they are needed the most. In addition, Smart Antennas enhance 5G application and service mobility by facilitating a more continuous connection, which may become particularly useful at 5G coverage seams. Otherwise, a 5G enabled user experience may degrade as hand-over from 5G to LTE occurs.
Once 5G networks are operational, continuous Voice over NR (Vo5G) coverage will be facilitated by directing RF where it is needed: communications. In absence of 5GNR for VoNR coverage, Vo5G calls will need to hand-over to LTE, analogous to how LTE hand-over to 3G was accounted for in 4G deployments. However, there is a big difference. Unlike LTE, which is becoming increasingly ubiquitous (especially in metro areas), 5GNR will be more constrained and thus needing Smart Antennas to direct RF signals to optimize end-user quality of experience for VoNR.
InvisiLight® Solution for Deploying Fiber
April 2, 2022Go to Market Faster. Speed up Network Deployment
April 2, 2022Episode 10: Fiber Optic Closure Specs Explained…
April 1, 2022Food for Thought from Our 2022 ICT Visionaries
April 1, 2022How Do Smart Antennas Work?
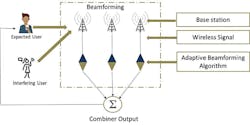
Smart Antennas use a few key technologies to improve 5G capacity and coverage. One such technology is beamforming in which RF energy is focused in a narrow beam to exactly where it is needed rather than emanating the same energy in a broad area. Beamforming is especially useful for 5GNR as the higher frequency mmWave RF is subject to fading over distance and attenuation loss caused by hitting objects (buildings, cars, foliage, etc.). A more directed beam of RF energy helps to ensure a greater probability of optimal bandwidth and signal quality. However, it is important to note that line of sight is still an issue as beamforming advantages are diminished with attenuation.
Another technology leveraged is multiple antennas (e.g., antenna arrays), which use Multiple Input/Multiple Output (MIMO) at both the source (transmitter) and the destination (receiver) to improve signal quality. This is in contrast to non-array systems in which a single antenna (and signal path) is used at the source and the destination.
MIMO/MIMO is advantageous as multiple signal paths can compensate for attenuation. A given path may experience signal gain while another attenuates or is blocked altogether. Optimal signals will change frequently during the course of a given 5G data or voice connection, meaning that the best signal will change from antenna to antenna in an antenna array.
Smart-Antennas-Supported 5G Application Use Cases
There are many 5G-enabled applications that will benefit from Smart Antennas, many of which require ultra-reliability and ultra-low latency. Mind Commerce 5G smart antenna market research points towards 4 application use case areas that will benefit greatly from Smart Antenna operation: public safety, robotics, connected vehicles, and drones. In addition, the market research firm sees Smart Antennas used most frequently in an urban environment and critical for support of many Smart City solutions.
Application Use Case Area #1
Mission Critical Communications
The public safety community increasingly relies upon IP-based solutions for first responder (ambulance, police, and fire) and dispatch communications as well as overall coordination in the event of a disaster. Accordingly, the market for mission critical public safety related communications is rapidly developing as developing technologies supply solutions necessary to meet emerging demand for improved voice, data, and machine-oriented communications.
Application Use Case Area #2
Industrial Automation and Robotics
Robotics is increasingly used to improve enterprise, industrial, and military automation. In addition, robots are finding their way into more consumer use cases as the general public’s concerns fade and acceptance grows in terms of benefits versus risks. Emerging areas for industrial robotics include robotics-as-a-service, cloud robotics, autonomous robotics, and general-purpose robotics. 5GNR will provide the bandwidth, reliability, and low-latency necessary to allow various industries to leverage the next phase of robotics evolution.
Application Use Case Area #3
Connected and Self-Driving Vehicles
Connected vehicles leverage many different wireless communications technologies including WiFi, Satellite, LTE, and soon 5G. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) refers to a vehicle’s ability to communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure (traffic signals, buildings, kiosks/billboards, parking lots, etc.), and even pedestrians. V2X will benefit greatly from 5GNR as dramatically improved bandwidth and latency improvements enhance existing solutions and enable new applications. Self-driving vehicles require high-capacity, low-latency communications for safe operation.
Application Use Case Area #4
Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)
An aerial drone (unmanned aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicle or UAV) is any aircraft that operates without direct human intervention from within or on the aircraft. 5GNR is anticipated to be a major catalyst for expanded and richer UAV/Drone use cases. Greater capacity and significantly lower latency afforded by 5G enables improved control and more sustainable flight as well as a wealth of new applications and services.
For more information about Mind Commerce 5G smart antenna market research, please visit https://mindcommerce.com/reports/5g-smart-antenna-market.
About the Author

Gerry Christensen
Gerry Christensen is Principal Consultant with Wireless Waypoint, which provides consulting, management, advisory and expert services for the information and communications technology industry. Core competency areas are switching, signaling, and related technologies and solutions. Practice areas include strategy, business development, fractional and interim management. This includes legacy telecom/IT as well as emerging business models and ecosystems, network infrastructure, VoIP networking and IP based services, operational and business support systems.
For more information, and to connect with him, visit www.linkedin.com/in/gerrychristensen/.