Latest from Industry Trends & Research
SURVEY: AI Integration
SASE Growth Slows to 10% in Q2
Build America, Buy America (BABA)
What will be possible in the future once 5G is widely rolled out across the world? In a very short time, new applications of 5G and IoT technology in healthcare will be immediately apparent. Some of them, in fact, will be unseen but hugely beneficial.
Check out 8 of the possibilities.
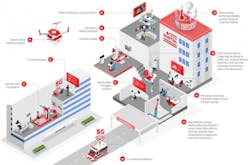
Remote Assisted Surgery and Training
5G’s high capacity and low latency (reducing the delay to less than 10 milliseconds making the transfer a near real-time interaction) means it can enable surgeons to use augmented reality (AR) technology to provide remote expert guidance on surgery without needing to be in the same operating theatre — or even the same country.
AR technology allows surgeons to interact with their colleagues remotely; for example, via AR video feed, their hands can be superimposed on the patient’s anatomy to give guidance during the operation, and they can overlay sketches and anatomical diagrams for reference.
The same technology can be used to carry out training remotely, with students able to access teaching in real time from expert teachers who are not able to be physically in the same room as them.
In both cases, the technology makes it easier to connect clinicians and access expertise from around the world.
Drones
Drones can be used to transport vital medical assets, including organs for transplant, medical equipment, and drugs, both more quickly and more cheaply than by courier.
In July 2020, Vodafone announced a partnership with Skyports and Deloitte to use drones to transport medical supplies for NHS Scotland. Supplies, including medicine, personal protective equipment (PPE), and COVID-19 testing kits, were flown to hospitals. Satellite-guided drones flying along pre-defined routes, cut transport times — from as long as 48 hours to just 30 minutes.
Drones provide a significant cost saving too: a report by WPI Economics on behalf of Vodafone earlier (in 2020) found that, on average, it is 95% cheaper to use drones than couriers for transportation.
InvisiLight® Solution for Deploying Fiber
April 2, 2022Go to Market Faster. Speed up Network Deployment
April 2, 2022Episode 10: Fiber Optic Closure Specs Explained…
April 1, 2022Food for Thought from Our 2022 ICT Visionaries
April 1, 2022Data Sharing
The massively increased speed and capacity of 5G compared to 4G means that very large files, such as MRI scans, can easily be shared securely for review between clinicians in real time, enabling more patients to be moved along the care pathway more quickly.
5G-Connected Ambulances
5G connectivity can link paramedics working with a patient in an ambulance with a hospital clinician using high-resolution video and tools that share the patient’s medical records as well as live clinical data such as heart rate.
• Clinicians can examine the patient remotely, assess symptoms, perform initial diagnosis, and prescribe urgent treatment that the paramedics can carry out before the patient even arrives at the hospital.
• Ambulance staff can use augmented technology (AR) support with AR glasses to follow specific treatment plans.
• The information sent to the hospital enables staff there to prepare the right treatment before arrival and save time — and lives.
Asset Tracking
Every time equipment (from wheelchairs to laptops to bed linen) goes missing, it costs money. Low-cost trigger tags on assets, combined with a series of beacons which constantly monitor where they are, means they can be found if they go missing or tracked if they are stolen.
The technology can also be used to monitor stock levels for drugs and assets and track them across the supply chain, and to help understand how often equipment is used to manage resources and capacity, as well as helping medical staff locate equipment rapidly in an emergency.
Smart Buildings
IoT devices can be used in buildings to monitor how space is used, and ensure that energy is used only where it is needed.
• For example, technology such as smart heating and ventilation systems can ensure that only spaces that are occupied are using energy by being heated or cooled.
• Motion sensors can facilitate smart lighting, ensuring that again only occupied spaces are lit and to the correct levels.
• And smart buildings can learn about occupancy patterns and suggest how they can be optimized for both workforce comfort and energy efficiency.
In hospitals, this could make a huge difference, both in how the buildings are used and to how much has to be spent on energy bills, as well as cutting hospitals’ contributions to greenhouse gas emissions.
Heat Detection Cameras
The Vodafone Heat Detection Camera can screen the body temperature of patients, visitors, and staff, to help provide reassurance at a time of concern about COVID-19 infection, but also beyond. Intelligent thermal and HD camera technology is used to discreetly and accurately screen up to 8 people at a time and 100 people per minute.
Social and Technological Prescribing
Technology such as wearable devices and monitoring systems can help people stay healthy by living more active lifestyles, and support those with chronic conditions.
Like this Article?
Subscribe to ISE magazine and start receiving your FREE monthly copy today!
Technology can also help alleviate loneliness in older and more vulnerable people by keeping them in touch with their family and friends.
Prescribing schemes that enable GPs and other health service practitioners to prescribe the use of wearables and other technology can support health and independent living.