Future Horizons and Cyber-Resiliency
The $$$ Value at Stake Is Staggering:
A series of digital, industry, and customer trends is accelerating digital transformation across the telecommunications industry. Customer expectations are crossing industry boundaries, and raising the bar across industries, forcing telecom operators to redefine customer experience. In addition, the pressures on traditional revenues are requiring operators to look at new digital business models and service areas, with areas such as IoT emerging as a battleground.
4 Digital Themes
Our analysis has identified 4 digital themes we expect will have the greatest impact on digitization in the industry over the next decade.
Theme 1: Networks of the Future
Virtualization and an abstraction of the physical hardware layer promise to fundamentally change the basis of future technological differentiation by creating networks that will be self-aware, self-optimizing, self-healing and self-secure.
Theme 2: Beyond the Pipe
The increased digitization of consumers and businesses presents the telecom industry with important opportunities to extend revenue streams beyond just connectivity — through IoT, digital services, and entirely new models of digital communication.
Theme 3: Redefining Customer Engagement
To win the race for customer loyalty and mindshare, the telecom industry will need to increasingly deploy features and tools that deliver delightful digital experiences. This is especially important as customers now expect the high-quality service they receive in one industry to be matched by companies in other sectors.
Theme 4: Bridging the Gap on Innovation
The need for rapid innovation, greater convergence and new services means that telcos must fill key capability gaps using new innovation models and revamped talent strategies for a digital workforce.
Within each theme is a set of tangible digital initiatives, which companies can implement to drive digitization forward. Despite new competitive pressures, digitization represents a significant opportunity for the telecom industry to create value.
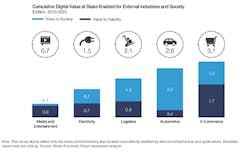
The impact of these 4 themes will be immense, with more than $2 trillion in value at stake for industry, consumers and wider society over the coming decade. (See Figure 1.) Of this, the value to the telecom industry could exceed $1.2 trillion in cumulative operating profit from 2016 to 2025, with initiatives under 2 of the themes, Networks of the Future and Beyond the Pipe, representing the largest-value opportunities. These themes also stand to create more than $800 billion in value for society and consumers, the majority of which will come from efforts to connect the billions of people still unconnected to the Internet. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
Cyber-Resilience falls within the network of the future theme. And recently, the scale of cyberattacks has been increasing globally at an alarming rate.
• >1 billion records of personally identifiable information stolen in 2014.
• $3.8 million Average total cost of a data breach, up 23% from 2013 to 2015.
The costs associated with this growing threat are already significant, and could rise in the future. A World Economic Forum study found that more frequent cyberattacks could result in a backlash against digitization. The report’s authors argued that, if attacker sophistication outpaces defender capabilities, resulting in more destructive attacks, a wave of new regulations and corporate policies could slow innovation. They estimate this could result in a negative economic impact of about $3 trillion by 2020.
Telecom operators find themselves at the forefront of this battle, and increasing risks point to greater responsibility for operators to ensure a secure global Internet. Though the percentage of total attacks on networks is marginal, the industry can play a key role in integrating cyber-resilience measures across network hardware, software, applications and end-user devices. A powerful call to action is likely to come from regulators looking increasingly to telecommunications, and the wider information and communications technology industry, to lead efforts to ensure global data privacy and security.
Cyberattacks pose a significant threat, but cybersecurity also presents an important opportunity for the industry as carriers of global internet data. Recognition of new risks means that global information security spend is likely to exceed $100 billion by 2019, creating an opportunity for individual operators and vendors to provide important security services. At a wider industry level, collaboration between operators can lead to greater resilience and new business opportunities. Three examples of this are shared in the short case studies below.
Case Study: GSMA Mobile Connect
The GSMA, the industry body for mobile operators, has spearheaded the effort to develop an industry-wide solution to help consumers take greater control of securing their data. The Mobile Connect authentication service is available to network operators globally and enables users to create and manage a digital universal identity via a single login. The service securely authenticates users, enabling them to digitally confirm their identity and their credentials, and grants safe access to mobile and digital services, such as e-commerce, banking, health, digital entertainment, and e-government. In this way, the GSMA is helping operators fulfill an important role in customer identity, while also enhancing customer convenience and experience by removing the need to remember multiple passwords.
Case Study: Lookout
Smaller companies and start-ups are also showing how digital technologies such as machine-learning and artificial intelligence (AI) can help companies build up cyber-defense mechanisms in line with the growing threat and complexity of attackers. Lookout, a Silicon Valley-based mobile security start-up, collects data from millions of mobile devices to continuously train its mobile security algorithms to detect and predict potential security risks and vulnerabilities. By creating a massive database of all mobile codes in the world, the company can deploy predictive algorithms at a scale that allows it to learn of new risks in real time and deflect attacks before they take place.
Case Study: Google
Other companies, such as Google, AT&T, Accenture, and Verizon, have focused on revamping internal security strategies to increase cyber-resilience. Google has recently moved all its corporate applications to the Internet. It is breaking away from the idea of a secure internal network protected by perimeter firewalls to one where user access to corporate functions is encrypted and protected at a device-and user-level. Employees can access corporate functions only from devices that are authenticated and, at the next layer, have to provide specific user authentication. This approach helps administrators control access and monitor individual users and devices, and protects other parts of the network in case of a breach.
Value-at-Stake Impacts
As consumers shift a larger share of their personal lives to the digital sphere, they are becoming increasingly careful about whom they trust with their information. Increased cyber-resilience is likely to create value for operators and device manufacturers in 2 key ways.
First, efforts to reduce the direct and indirect costs associated with data breaches (e.g., curbing losses of sensitive information, faster remediation, and minimizing damage to business continuity) could lead to direct cost savings of almost $80 billion.
Second, efforts to increase cyber-resilience and establish greater trust with consumers in data security is likely to drive market-share shifts within the industry. We estimate these shifts to be worth $70 billion in value migration across operators and device manufacturers. However, we project that increased information security costs could equate to more than 2% of revenue by 2025, offsetting some of these cost savings.
Customers are likely to benefit from reduced costs associated with the loss of personal information through fraudulent transactions. They will also need to spend less time resolving these incidents as cybersecurity measures reduce incidences of fraud. We calculate that these benefits translate into savings of up to $60 billion for consumers globally.
Greater annual spend on information security is likely to increase the demand for professionals in this area. It is estimated that thousands of roles could be created across the industry to support companies’ cyber-resilience efforts, with some of them filled by reskilled employees from other areas. (See Figure 3.)
Figure 3.
All figures cumulative for period 2016-2025:
$100 billion value addition for the industry
$60 billion value addition for consumers and society
$29 billion value addition for external industries
Save
Save
Save