Latest from Network Transformation/Edge Compute/IoT/URLLC/Automation/M2M
mHealth Requires Network Health
Remotely Monitored Patients to Grow 47.9% by 2021:
Berg Insight says 7.1 million patients worldwide were remotely monitored in 2016. That number grew 44% over the year prior. This illustrates how the mHealth market has entered a growth phase fueled by rising market
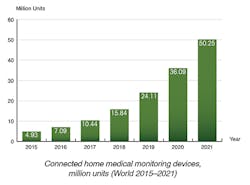
acceptance in several key verticals. This number includes all patients enrolled in mHealth care programs in which connected medical devices are used as a part of the care regimen. We estimate that the number of remotely monitored patients will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 47.9% to reach 50.2 million by 2021. (Connected medical devices used for various forms of personal health tracking are not included in this figure.)
The 2 main applications are monitoring of patients with sleep therapy devices and monitoring of patients with implantable cardiac rhythm management (CRM) devices. These 2 verticals accounted for 80% of all connected home medical monitoring systems in 2016. The number of remotely monitored sleep therapy patients grew by 70% in 2016, mainly driven by Resmed that has made connected healthcare a cornerstone of its strategy. Other leading vendors in this segment are Philips Respironics and SRETT. The CRM market is led by companies such as Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and St. Jude Medical (now Abbott) that included connectivity in CRM solutions more than a decade ago.
Telehealth is the third largest segment with 0.50 million connections at the end of the year. Leading telehealth hub vendors include Tunstall Healthcare, Honeywell, Cardiocom, Philips, and Qualcomm Life. All other device categories — including ECG, glucose level, medication adherence and others — stood for less than 1 million connections together.
Cellular connectivity has already replaced the PSTN as the de facto standard communication technology for most types of connected home medical monitoring devices, and will account for 25.2 million connections in 2021. The number of mHealth devices with integrated cellular connectivity increased from 3.0 million in 2015 to 4.9 million in 2016.
The use of BYOD connectivity will increase the most during the next 5 years, with a forecasted CAGR of 109%. BYOD involves low costs, but cannot be used to reliably connect every patient. BYOD connectivity will be preferred by select patient groups and will be used for the remote monitoring of 22.9 million patients in 2021. The technology will be most useful for patient-centric engagement programs in therapeutic areas such as diabetes and asthma, that have younger patient demographics compared to many other chronic diseases. In fact, many of these patients will prefer to use their own smartphone as the interface instead of carrying around a dedicated device for remote monitoring.
Save
Save